|
|
|---|
Caution: Iliopsoas tendonitis after total hip arthroplasty may be more common than acknowledged: Do not flex your hip more than 90
degrees without the consent of your surgeon!
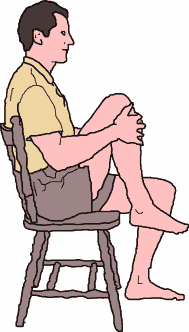
The Seated Knee Raise:- Start Position
- Sit on a chair or comfortable seat with your back supported.
- Let your lumbar spine flex a little so that your pelvis is "looking upward".
- Use your hands to bring your right leg up to the flexed position, and release the leg.
- Scapulas anchored and head buoyant on top of your spine.
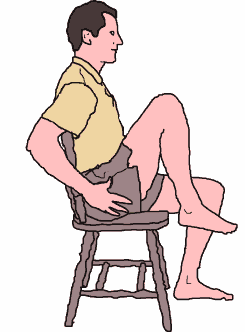
The Seated Knee Raise:- Action
- Breathe in and zip and hollow.
- (Breathing out): Raise your right knee and hold.
- Breathe in and maintain zip and hollow.
- (Breathing out): Lower your right knee (small movement - about 5 cm).
- Repeat four to 10 times.
Comments
Option: You can make this exercise harder by pushing down with your left hand on your knee.
Stretch and trigger point your hip flexor muscles before and after this valuable exercise! -
See:
The Safe Psoas and Hip Flexor Stretch, also
Triggerpoint Therapy Workbook....
(iliopsoas, tendonitis, bursitis, pilates exercise, Scroll right>>>...)
© Bruce Thomson, EasyVigour Project
scroll up^^^^.....
|
The Seated Knee Raise:
Start Position
Action
|
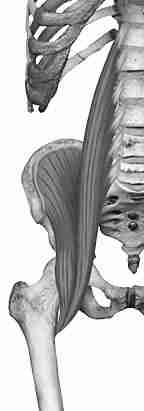
Pictures:
The Iliopsoas muscles
The Tensor Fascia lata and Sartorius

|
|
What it does
- Works the Iliopsoas muscle in preference to the Tensor fascia lata, thereby minimizing hip medial
rotation(1).
- The specific body positioning and Pilates style bracing protects the lumbar spine
from the compressive forces of the Iliopsoas muscle.
- According to Sahrmann(1), a strong Iliopsoas aids in preventing forward glide of the femoral head
in the hip socket, which is the "directional susceptibility of motion"
associated with hip & groin pain due to iliopsoas tendonitis/ bursitis, & acetabular labral tears.
(See also ref. 3)
Watch Points
- Keep all other leg muscles relaxed. This is a skill rather than a strength exercise!
- Keep the upper body relaxed.
- Make sure that the hips do not twist to the side.
Reference
- Shirley A Sahrmann: Diagnosis and Treatment of Movement Impairment Syndromes;
Publ. Mosby 2002 ISBN 0-8016-7205-8
- Consequences of Office Chair Sitting(3): Tight Hamstrings,
Iliopsoas Trigger Points, Erector Spinae Muscle Fatigue.
- Harding L, Barbe M, Shepard K, Marks A, Ajai R, Lardiere J, Sweringa H:
J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2003 Mar;33(3):118-25:
Posterior-anterior glide of the femoral head in the acetabulum: a cadaver study.
|



